Reports
Nextflow provides several reporting mechanisms to analyze and debug pipeline runs:
Execution log: Command to query information about past runs
Execution report: Comprehensive HTML report for a pipeline run
Execution timeline: HTML timeline of tasks executed in a pipeline run
Trace file: CSV file with detailed task metrics for a pipeline run
Workflow diagram: Graph visualization of pipeline structure
Execution log
The nextflow log command shows information about past pipeline runs and task executions. You can query by run name or session ID, and the command provides multiple options to filter and format the output.
By default, nextflow log prints the list of pipeline runs:
$ nextflow log
TIMESTAMP DURATION RUN NAME STATUS REVISION ID SESSION ID COMMAND
2025-12-09 11:43:18 1s naughty_heisenberg OK 2ce0b0e294 bae65ec6-a2b9-49bf-b63e-2fec91945e48 nextflow run hello
2025-12-09 11:43:28 931ms thirsty_swanson OK 2ce0b0e294 bae65ec6-a2b9-49bf-b63e-2fec91945e48 nextflow run hello -resume
2025-12-09 11:43:37 8.5s goofy_kilby OK ca20a6dfd2 d0a60572-076e-451a-b10e-16059ed77e36 nextflow run rnaseq-nf -profile conda
Providing a run name or session ID prints the tasks executed by that pipeline run:
$ nextflow log goofy_kilby
/Users/user/workspace/work/e1/fc2d06782f8263476426c576888033
/Users/user/workspace/work/72/f0542cfa81ad6abeaf1adf02e5cc2b
/Users/user/workspace/work/83/009346a3958358bb704e996d935c7a
/Users/user/workspace/work/84/15e4cd16df1db6f9bc0e22cc05316d
Customizing fields
The -f (-fields) option specifies which fields to include in the log.
nextflow log <run_name> -f [fields]
You can set a custom list of fields to focus on specific information. For example, hash, name, exit, and status:
$ nextflow log goofy_kilby -f hash,name,exit,status
e1/fc2d06 RNASEQ:INDEX (ggal_1_48850000_49020000) 0 COMPLETED
72/f0542c RNASEQ:FASTQC (ggal_gut) 0 COMPLETED
83/009346 RNASEQ:QUANT (ggal_gut) 0 COMPLETED
84/15e4cd MULTIQC 0 COMPLETED
Run the log command with the -l option to see the full list of fields. See log for more information.
Templates
The -t option specifies a template (string or file) to use when inspecting a single run:
nextflow log <run_name> -t <template> > <report>
You can create a template. For example, in Markdown:
## $name
script:
$script
exit status: $exit
task status: $status
task folder: $folder
Then, use it to create a report:
nextflow log goofy_kilby -t my-template.md > execution-report.md
Filtering
The filter option selects which entries to include in the log.
nextflow log <run_name> -filter '<filters>'
Any valid Groovy boolean expression on the log fields can be used to define the filter condition. For example, you can filter for task names matching a pattern:
nextflow log goofy_kilby -filter 'name =~ /hello.*/ && status == "FAILED"'
Execution report
The execution report is an HTML report that includes metrics about a pipeline run. The report is organized into three sections: Summary, Resources, and Tasks.
To enable the execution report, add the -with-report option when launching a pipeline run:
nextflow run <pipeline> -with-report [file_name]
You can also enable the report in your Nextflow configuration:
report {
enabled = true
file = 'report.html'
}
See report for the list of available config options.
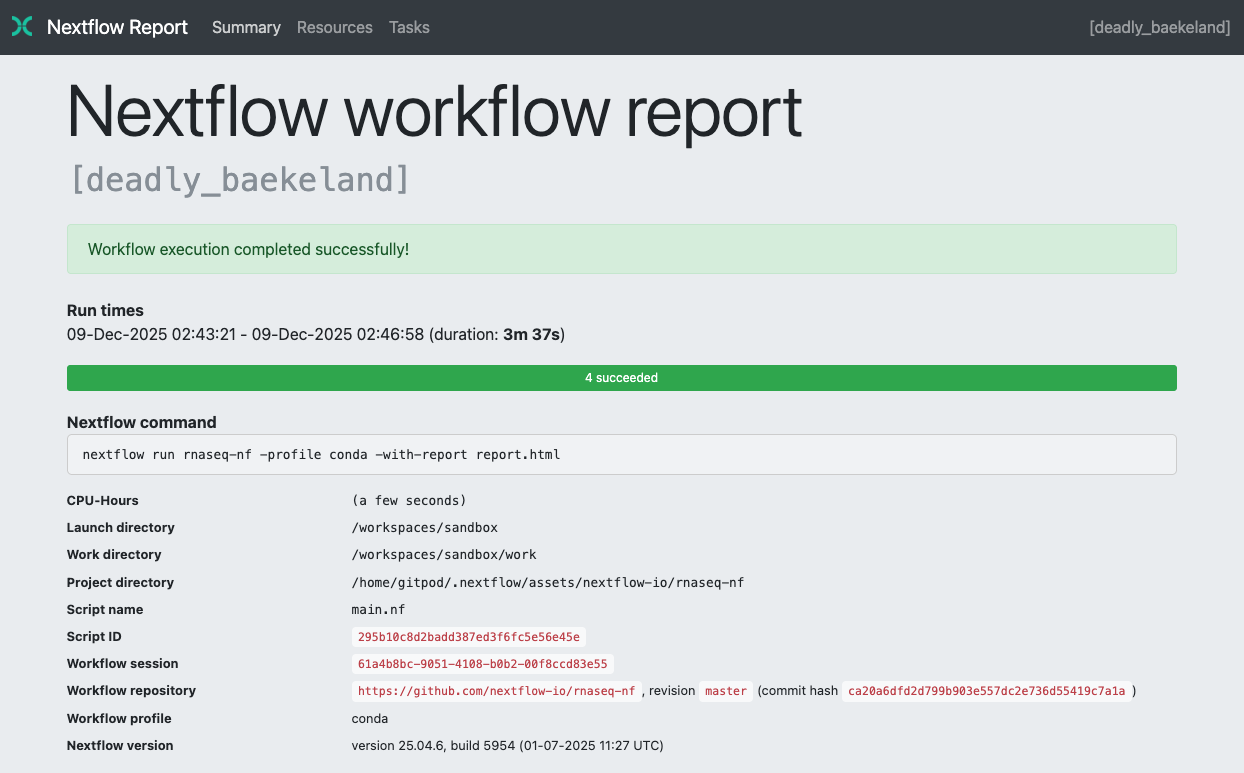
Summary
The Summary section reports the execution status, the launch command, overall execution time, and other workflow metadata:
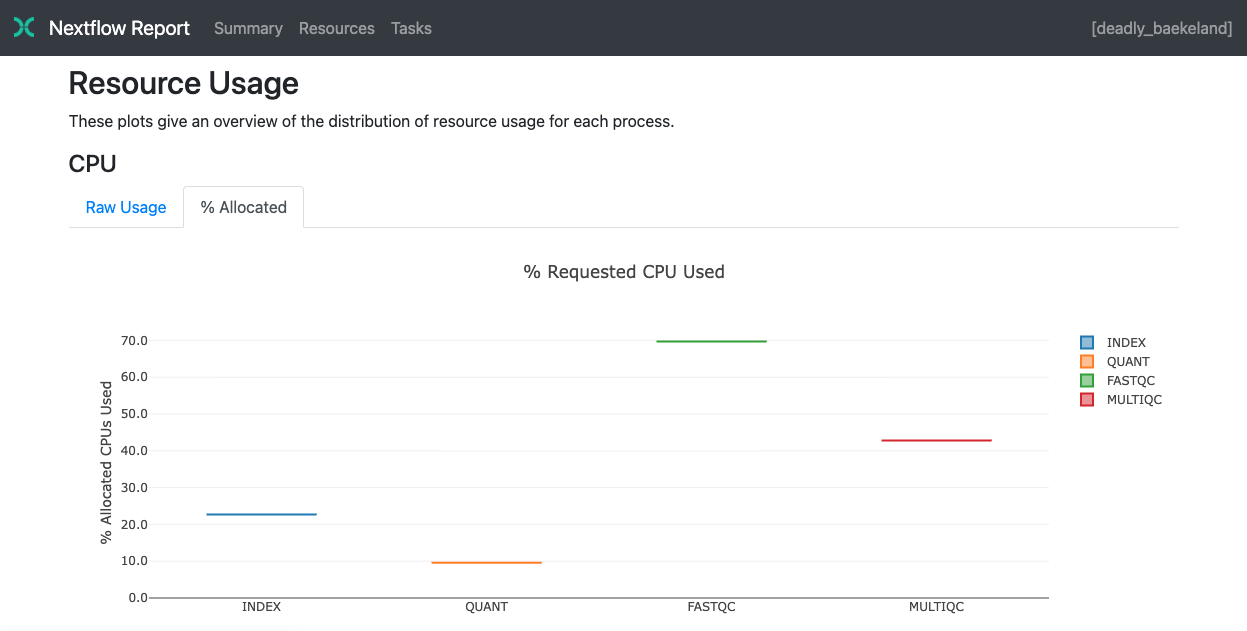
Resource usage
The Resources section plots the distribution of resource usage for each workflow process using the interactive plotly.js plotting library.
Plots are shown for CPU, memory, job duration, and disk I/O. Each usage metric is shown both in raw form and as a percentage of the requested resources. These plots are helpful to check that task resources are used efficiently.
For information about how resource usage is computed, see Understanding task resource metrics.
Tasks
The Tasks section lists all executed tasks, reporting the status, command script, and other metrics for each task:
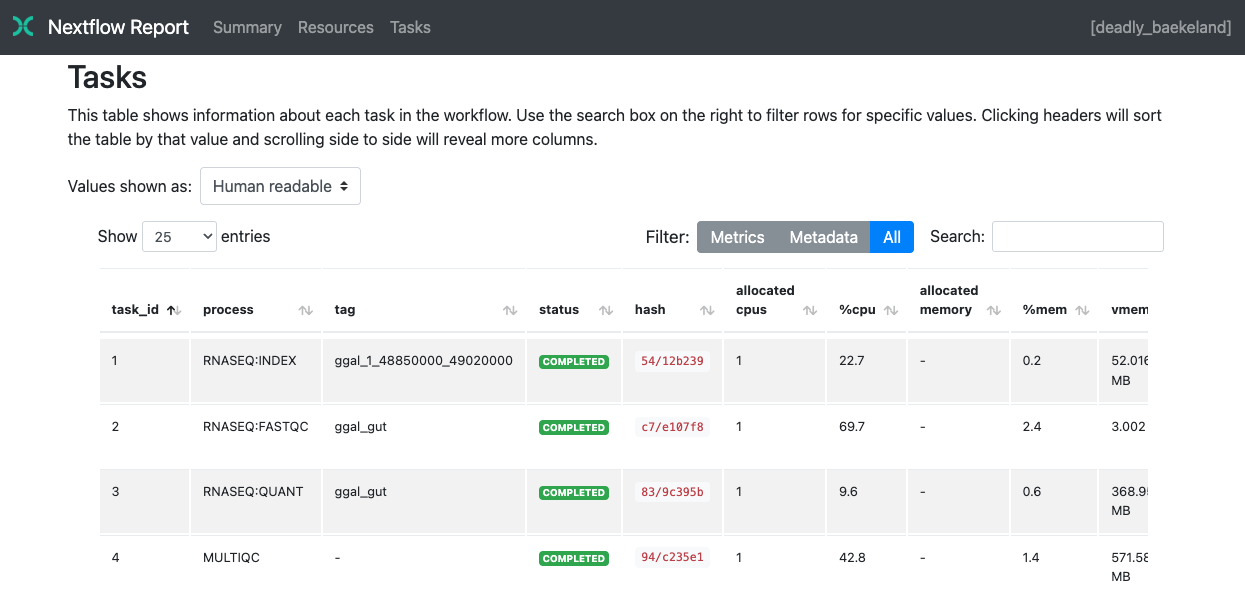
The same caveats for the trace file also apply to the task table.
Execution timeline
The execution timeline is an HTML report that shows a timeline of the tasks executed in a pipeline run:
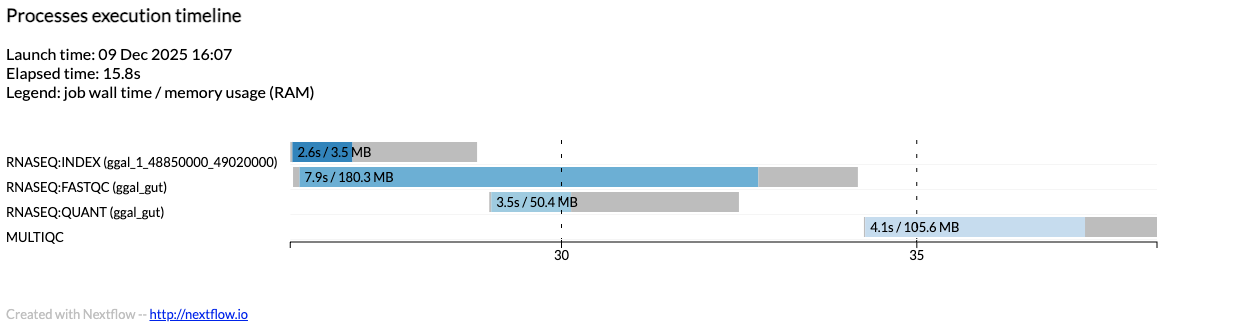
The x-axis shows elapsed time relative to workflow launch. The y-axis shows a bar for each task execution. Each bar has the following properties (with the equivalent trace fields in parentheses):
Bar length: Task duration (
duration)Bar color: Identifies tasks from the same process
Colored area: Real execution time (
realtime)Gray area (left): Task scheduling time (
start - submit)Gray area (right): Task termination time (
complete - start - realtime)Label: Task duration (
duration) and peak memory usage (peak_rss)
To enable the execution timeline, add the -with-timeline option when launching a pipeline run:
nextflow run <pipeline> -with-timeline [file_name]
You can also enable the execution timeline in your Nextflow configuration:
timeline {
enabled = true
file = 'timeline.html'
}
See timeline for the list of available config options.
Trace file
The trace file is a CSV file containing information about each task executed in a pipeline run, including submission time, start time, completion time, CPU usage, and memory usage.
To create the trace file, add the -with-trace option when launching a pipeline:
nextflow run <pipeline> -with-trace
The above command creates a file named trace.txt in the current directory. For example:
task_id |
hash |
native_id |
name |
status |
exit |
submit |
duration |
realtime |
%cpu |
peak_rss |
peak_vmem |
rchar |
wchar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 |
45/ab752a |
2032 |
blast (1) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:33:16.288 |
1m |
5s |
0.0% |
29.8 MB |
354 MB |
33.3 MB |
0 |
20 |
72/db873d |
2033 |
blast (2) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:34:17.211 |
30s |
10s |
35.7% |
152.8 MB |
428.1 MB |
192.7 MB |
1 MB |
21 |
53/d13188 |
2034 |
blast (3) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:34:17.518 |
29s |
20s |
4.5% |
289.5 MB |
381.6 MB |
33.3 MB |
0 |
28 |
b4/0f9613 |
2041 |
exonerate (1) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:38:19.657 |
1m 30s |
1m 11s |
94.3% |
611.6 MB |
693.8 MB |
961.2 GB |
6.1 GB |
31 |
d7/eabe51 |
2042 |
exonerate (3) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:45:50.846 |
3m 1s |
2m 6s |
130.1% |
703.3 MB |
760.9 MB |
1.1 TB |
28.6 GB |
30 |
4f/1ad1f0 |
2043 |
exonerate (2) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 16:45:50.961 |
10m 2s |
9m 16s |
95.5% |
706.2 MB |
764 MB |
1.6 TB |
172.4 GB |
52 |
72/41d0c6 |
2055 |
similarity (1) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 17:13:23.543 |
30s |
352ms |
0.0% |
35.6 MB |
58.3 MB |
199.3 MB |
7.9 MB |
53 |
3e/bca30f |
2061 |
similarity (2) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 17:13:23.770 |
30s |
238ms |
0.0% |
6.7 MB |
29.6 MB |
190 MB |
91.2 MB |
54 |
8b/d45b47 |
2062 |
similarity (3) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 17:13:23.808 |
30s |
442ms |
0.0% |
108.1 MB |
158 MB |
832 MB |
565.6 MB |
98 |
de/d6c0a6 |
2099 |
matrix (1) |
COMPLETED |
0 |
2014-10-23 17:14:27.139 |
30s |
1s |
0.0% |
4.8 MB |
42 MB |
240.6 MB |
79 KB |
The following caveats apply to trace metrics:
Nextflow collects trace metrics through a background process for each job in the target environment. Make sure the following tools are available in the environment where tasks are executed:
awk,date,grep,ps,sed,tail,tee. Container images that do not include all of these tools may lead to missing data.Trace metrics provide an estimation of the resources used by running tasks. They are not an alternative to low-level performance analysis tools, and they may not be accurate for very short-lived tasks (e.g., less than a few seconds).
Some trace metrics are not reported when running on macOS.
You can also enable the trace file in your Nextflow configuration:
trace {
enabled = true
file = 'trace.txt'
}
See trace for the list of available config options.
Workflow diagram
A Nextflow pipeline can be represented as a directed acyclic graph (DAG). The vertices in the graph represent the pipeline’s processes and operators, while the edges represent the data dependencies (i.e., channels) between them.
To render the workflow DAG, run your pipeline with the -with-dag option. By default, it creates a file named dag-<timestamp>.html with the workflow DAG rendered as a Mermaid diagram.
The workflow DAG can be rendered in a different format by specifying an output file name with a different extension based on the desired format. For example:
nextflow run <pipeline> -with-dag flowchart.png
Tip
Use the -preview option with -with-dag to render the workflow DAG without executing any tasks.
The following example shows the Mermaid diagram for the rnaseq-nf pipeline (using the Mermaid Live Editor with the default theme):
nextflow run rnaseq-nf -preview -with-dag
See dag for the list of available config options.